As the line between frontend and backend has blurred over the past few years (thanks React), the JAMStack has emerged as a new paradigm for building sites and apps. The stack itself is generally easy to understand, but the ecosystem – tools, plugins, and APIs – isn’t. I am going to walk through
1) What the JAMStack is ?
2) How to categorize tooling?
3) Architecture of JAM Stack.
4) Why modular use case specific APIs are going to continue to grow in popularity.
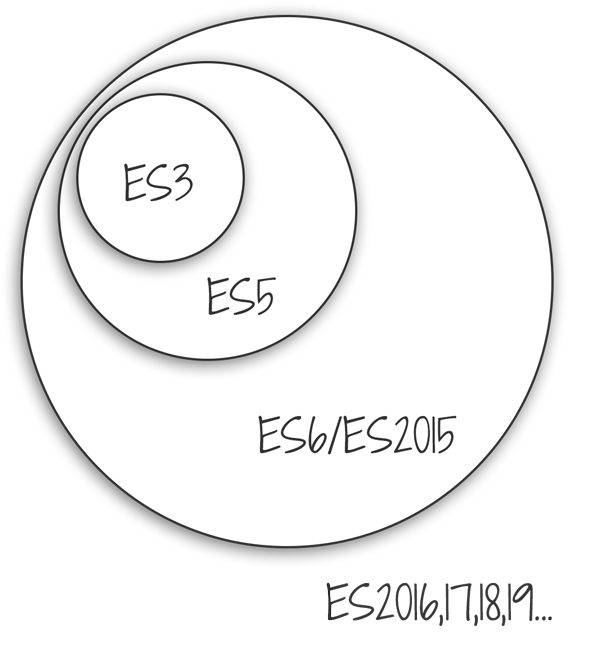
JAVASCRIPT, API, AND MARKUP
The JAMStack is an architectural pattern (sort of) for building apps that moves away from the traditional web server model and focuses on serving static files from “the edge” (data centers physically close to your computer). JAM stands for Javascript, API, and Markup:
- Javascript: all code is in JS, for both frontend interactivity and API requests and handling
- API: instead of a monolithic web server, all backend functionality (authentication, users, etc.) is served via APIs
- Markup: your whole site is just a bunch of HTML files served statically
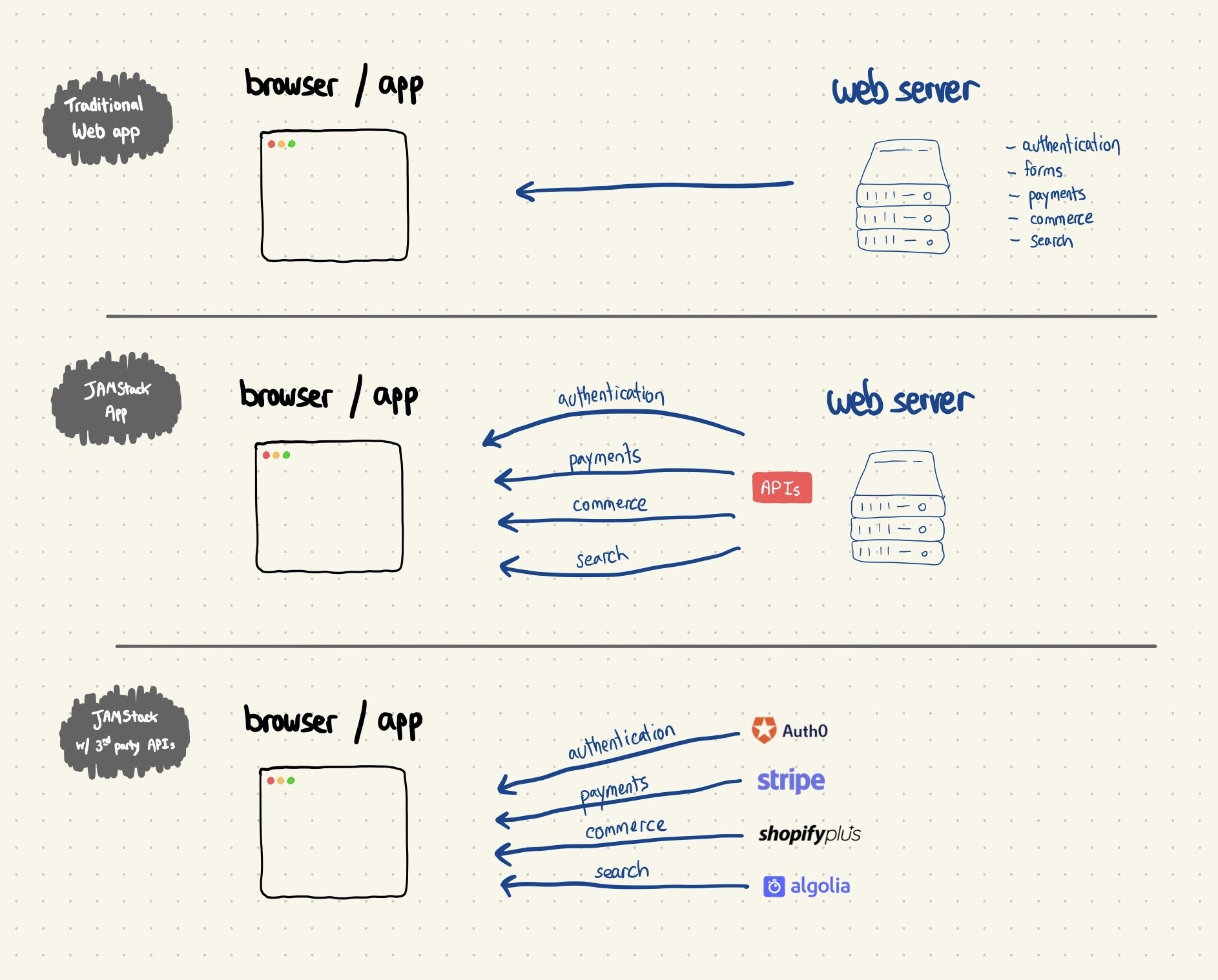
This is like, very different from what most larger apps look like. If you’re accessing a web app like Twitter in your browser, there’s probably a ton of server side logic dictating what you see, how you log in, and everything else that’s custom about your experience. In a JAMStack app, all of that logic would be encapsulated in simple APIs.
These ideas have been around for a while, but the JAMStack concept is definitely having a moment over the past couple of years:
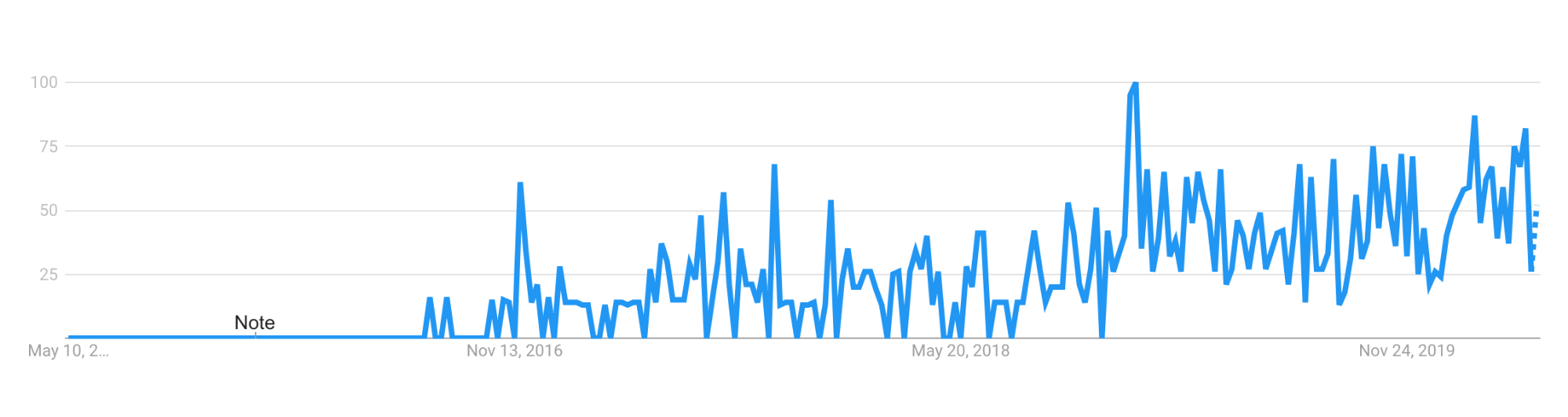
There’s even a JAMStack conference that started in 2018, started by a group of repeat founders from early JAMStack companies (Contentful, Gatsby, etc.) that have continued investing in the ecosystem.
The past few years have been a perfect storm for the kind of apps we’re talking about. Javascript is now the most popular programming language in the world, used by 70% of devs last year and likely more in 2020. GraphQL is used by almost 40% of JS devs, and even Apollo by 25%. Hosting has gotten laughably cheap, and services like Netlify give you automatic deploys, a global CDN, and authentication for free.
As with everything in web development, JAMStack apps vs. traditional web apps isn’t entirely black and white. Even if you hide complex server logic behind easy to use APIs, JAMStack apps need to have a backend somewhere; and caching and serving files from a CDN isn’t exactly a new idea.
Think of JAMStack less as an architecture and more as a philosophy for where application logic should sit and what best practices for serving sites should be. In that vein, keep an eye out for Redwood.js – they’re taking aim at a full framework for JAMStack apps complete with an actual backend.
THE JAMSTACK ECOSYSTEM
The easiest way to understand all of the available tooling out there is to break it down by JAM – Javascript, API, and Markup.
1. J is for Javascript
It’s a meme that Javascript is the worst, and some teams have been focusing on improving ergonomics by building on top of it. The best known example is Typescript – it’s basically strongly typed Javascript. The ability to define static types means you’ll be able to catch errors before your code runs. Static typing is standard in languages like Java and C++, and Python added pseudo-support last year. Another example of a related JS add-on: Purescript.
2. A is for API
Even if your backend is nice and clean and obscured behind a simple API, application logic has to live somewhere. The serverless ecosystem has been growing pretty quickly: all major cloud providers offer the ability to run functions without setting up a server, like Lambda on AWS. Over the past few years though, hosting providers like Netlify and Vercel have started to support serverless functions as add-ons. They’re both just white-labeling other cloud providers for now, but that could change in the future. AWS’s Amplify is lurking (along with ages old Firebase), too.
Another important area of the ecosystem is CMS providers. If you’re running a blog or publication, you’d traditionally need to use a Content Management System like WordPress or Drupal – deployed on a server – to write and manage your content. For JAMStack apps (or regular apps too, really), newer providers like Contentful and Storyblok expose content through REST or GraphQL APIs so you don’t need to manage any servers yourself. There are a lot of headless CMS solutions out there.
3. M is for Markup
This is where things get interesting. Probably the biggest story in frontend over the past few years has been the meteoric rise of client side rendering via React, Vue, and Angular. Building componentized pages that interact well with your data model is now more of a science than an art. Alongside these kinds of libraries, a new suite of static site generators like Hugo, Jekyll, Gatsby, and Next.js are making it simpler to go from content to built page.
The last missing piece here is hosting and deployment. Like Firebase did for mobile apps, companies like Netlify offer platforms that simplify a lot of the annoying parts of building JAMStack apps, like a global CDN, automatic deploys, identity and login, and serverless functions. More about them in the next section.

TWO TYPES OF TOOLS: POINT AND PLATFORM
As with pretty much all developer tools, the JAMStack landscape can be split into two basic approaches: do a really good job at one task, or offer a full platform for accomplishing an entire workflow.
→ Point solutions
Most of the tools we covered across the J,A, and M try to be useful for one particular task: Contentful for CMS, Lambda for Serverless, or Hugo for static site generation. You can’t realistically finish an entire project without using multiple of these, and they don’t necessarily integrate well out of the box.
→ Platforms
Companies like Netlify and Zeit are trying to build full platforms for building JAMStack apps – they take care of almost everything, from deploy to functions to CMS. Individually, each piece that they offer isn’t going to be the best on the market, or even close to that; but the power of features integrated together can sometimes outweigh shortcomings of individual products (just ask Microsoft). This is part of why Netlify is trying to own the content and narrative around JAMStack sites.
For an exhaustive list of JAMStack related tools, check out the awesome-jamstack repo on Github.
THE FUTURE: USE CASE SPECIFIC APIS
Earlier, we looked at tools like Contentful; they provide a fully managed CMS that gets exposed via an API. CMS is just one well scoped use case – writing and managing content. But the Contentful model is getting a lot more popular as a broader category: SaaS tools that take care of a full piece of a workflow with a very use case specific series of APIs. Here are a few examples of more established ones:
- Algolia – search as a service via configurable APIs
- Auth0 – identity and authentication as a service via API
- Optimizely – APIs for feature flagging and experimentation
- Shopify Plus – headless e-commerce, like Contentful
- Sendgrid – send emails to your users via API
- Stripe – IDK if you’ve heard of them, they’re hiring
These tools have 2 equally important parts:
- A series of APIs to integrate directly into your app
- A frontend / admin panel for visibility and management
Take a look at Algolia, for example. You push data, configure indices, and call search all via a client library like Javascript. Once you have the Algolia APIs working in your app, you can use their dashboards to get analytics and see how users are interacting with what you’ve built.
These services have nothing to with each other in terms of what they actually help developers do, but they all rely on the same approach of providing value through a narrowly scoped set of APIs (and they’re API first, even if there are frontends) that solve a particular functional use case.
One way of looking at these third party APIs is as a natural progression from JAMStack’s core tenet: couching complexity behind well designed APIs that make actual deployment easy. The next logical step is outsourcing those APIs.
I think this is going to become an increasingly common piece of how developers automate parts of their work. A few newer services I’m keeping an eye on:
- Memberstack – APIs for building and managing memberships
- Getform – APIs for building forms into your site with “no backend”
- Sendbird – APIs for chat and messaging in your app
- Snipcart – API for adding a shopping cart to your site
Some of these services are more infrastructure-y (think Plaid, Algolia) while some are more functional (Memberstack, Sendbird). The common thread is that they need to solve some non-trivial problem (if it’s too easy to build yourself, you will) while still giving developers the flexibility they’d expect from something more custom.
Thanks to spotify and yputube developer channel for some good ideas.
If you liked or hated this, share it on Twitter, Reddit, or HackerNews.